Wells and boreholes can be described by their depth, or by the way they are constructed. They may also use different types of pump at the surface to raise the water.
Shallow wells
Shallow wells and boreholes usually have a depth of less than 30 m, although they can be as much as 60 m deep, especially in very dry areas of the world where the water table is low.
Below is a diagram of a protected hand-dug well. Wells can be excavated by hand if the soil is not too hard or the water table is high. Hand-dug wells have a relatively large diameter because they have to be wide enough for a person to be able to stand inside and dig.
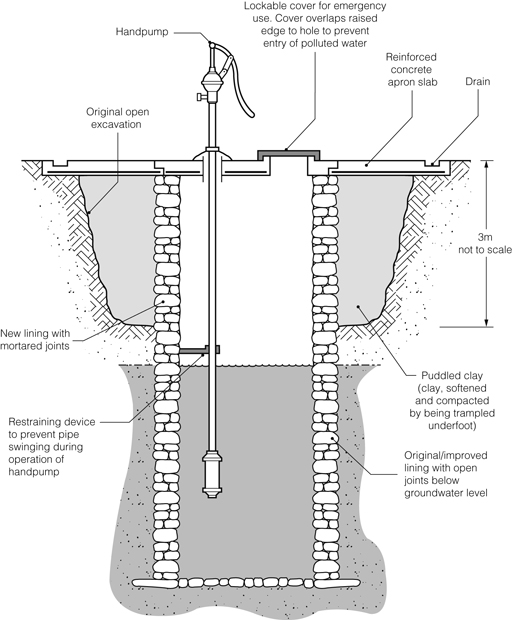
Diagram of a hand-dug well.
The inside wall of the top 3 m or so of the dug well should be made waterproof by constructing a well casing (lining). In small-diameter wells the casing can be a pipe, but in large wells the casing needs to be constructed in concrete from the top of the well down to a minimum depth of 3 m. The casing of the well should also be extended for a minimum of 60 cm above the surrounding ground level to prevent the entrance of surface run-off – that is, water that runs off the surface of the land, carrying debris, wastes and other pollutants with it as it flows. A concrete cover should be fitted over the well casing, as in Figure 3.5, to prevent dust, insects, small animals and any other contaminants from falling in.
Boreholes
Because there are many variables, there’s no fixed cost for drilling a water well with a professional bore hole company. However, a private water well, connected and providing running water could cost up to £23,000!
They first need to take into account:
- The geology of your area
- The depth we need to drill
- The width of the borehole
- Pumps and equipment
A borehole includes drilling down to the aquifer, this can be around 60-80m, but can vary quite a lot depending on your area’s geology.
Once the borehole is drilled it needs to be cased, sealed and lined.
A well screen is put in and above it a submersible pump. The pump lifts the water up through the rising main then along the discharge pipe to a pressure tank. The well water is stored in the pressure tank, where it goes on to supply your tap or building.
What is an aquafer?

| Definition: A diverse body of intercalated permeable and less permeable material that acts as a water-yielding hydraulic unit of regional extent. DescriptionAn aquifer system is a group of formations that contain sufficient saturated permeable material to yield economic quantities of water to boreholes and springs. Why are aquifer systems important? Aquifer systems are the storage medium from which groundwater is abstracted. They should be managed properly and at all times be protected from over-exploitation and contamination. |
At the time of writing this blog post I have not tried starting it yet as we are currently FLOODED! So will update when I get started.

